What is a Calcified Tooth?
A calcified tooth is also known as pulp canal obliteration or calcified metamorphosis. Calcified tooth often develops after trauma, extensive decay or as a result of ageing. The process involves the filling of the tooth and root canal with calcium deposits which obliterates the pulp or soft tissue inside the tooth. This results in replacing the soft tissue with hardened calcified tissue.
Causes of Tooth Calcification
Calcification is a natural response to damage to a tooth’s pulp or soft tissue. Several factors which contribute to this phenomenon are:
- Trauma and Injury: Often caused by sports injuries or accidents, resulting in calcium deposits to protect against further decay.
- Longstanding Decay: Decay in the root canal that expands beyond the enamel, eroding the pulp and leading to calcification.
- Ageing: Reduced blood supply to the tooth with age can contribute to the formation of a calcified cavity.
Symptoms of Calcified Tooth or Root Canal
Identifying symptoms of calcified teeth is important for seeking timely dental care. Some individuals may experience subtle signs while others may face more noticeable symptoms. Brief overview of symptoms associated with calcified teeth are:
Common Symptoms: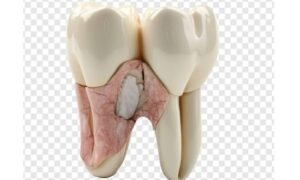
- Increased sensitivity to hot or cold temperatures.
- Discomfort or pain in the affected tooth.
- Changes in tooth color may be noticeable, often appearing darker.
Less Common Symptoms:
- Difficulty in moving the affected tooth.
- During a dental examination, a dentist may notice areas of unusual hardness.
Complications of Tooth Calcification
A calcified tooth can lead to various complications, posing challenges for standard root canal treatments. Key complications include:
- Calcified teeth are prone to infection, leading to severe pain and discomfort.
- The calcification alters the tooth’s appearance, often resulting in a darker color.
- Standard root canal treatments become challenging due to the structural changes caused by calcification.
Diagnosis of Calcified Tooth or Root Canal
Diagnosis of calcified tooth or root canal involves following steps: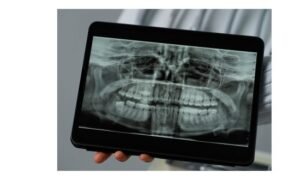
- Visual Inspection: Dentists visually examine teeth for discoloration, surface changes, and signs of calcification.
- Patient History: Understanding trauma, injury, or genetic factors provides valuable insights.
- Clinical Examination: Dentists use tactile feedback to identify variations in hardness during hands-on assessments.
- Digital X-rays: Guide dentists to calcified canals with precision, minimizing tooth structure removal.
- High-Powered Microscope: Aids in identifying almost invisible calcified canals, enhancing diagnostic accuracy.
Treatment of Calcified Tooth or Root Canal
A. Treatment Tools:
- Digital X-rays: They are essential for assessing the tooth and surrounding tissues.
- High-Powered Microscope: It helps in precise targeting of calcified canals during treatment.
- High-End Rotary System: It prepares the calcified tooth or root canal for treatment with a precision tool. It helps in preventing root canal fractures during treatment and facilitates work in restricted spaces.
B. Approaches to Treatment: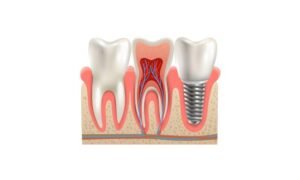
- Saving the Tooth: Endodontists aim to preserve the tooth and root canal whenever possible.
- Extraction: If saving the tooth is not viable tooth extraction may be considered in severe cases.
- Multi-Professional Collaboration: Dentists and endodontists work together to devise effective treatment plans.
FAQs
1. Can calcified teeth be treated?
Yes, seeking prompt help from a dentist is essential. Advanced tools like digital X-rays, microscopes, and high-end rotary systems aid in personalized treatments.
2. Is extraction the only solution for calcified teeth?
No, preserving the tooth is the primary goal. Extraction is only considered in severe cases. Your dentist will strive to save the tooth and root canal whenever possible.
3. How can one prevent tooth calcification?
Regular dental checkups, effective oral hygiene practices and wearing mouth guards during activities that pose a risk of dental trauma are key preventive measures against tooth calcification.
The Bottom Line
Understanding calcified tooth will help you to recognize your symptoms early. Timely visits to the dentist and advanced tools like digital X-rays and microscopes are helpful in devising tailored treatment plan. Main goal of the treatment is to save the tooth but in severe cases extraction might be necessary. Remember to follow oral health guidelines and visit your dentist regularly!
Disclaimer
Content on this site is written with thorough research and keeping in mind the latest guidelines. However, no content on this site should substitute professional consultation.
