Prediabetes means your blood sugar is higher than normal but not as high to be called as diabetes. It’s like a warning sign from your body, telling you to take care of yourself before things get serious. With some healthy changes like eating better and doing regular physical activity, you can stop it from turning into full blown diabetes. So, it’s like a chance to make things better before they get worse.
Table of Contents
What is Prediabetes?
- Prediabetes is a metabolic condition characterized by elevated blood sugar levels but not as high enough to be classified as full-blown diabetes.
- It is a warning sign that you have high risk of developing type 2 diabetes, which can have serious health implications.
Statistics:
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC):
- Approximately 88 million adults in the United States have prediabetes.
- Shockingly, 84% of people among this population are unaware of their condition.
- It affects people of all age groups. It’s prevalence increases with age.
Conversion of Prediabetes into Type 2 Diabetes:
Research shows that without intervention, a significant percentage of individuals with prediabetes progress to type 2 diabetes. Key statistics include:
- About 15-30% of people with prediabetes will develop type 2 diabetes within five years.
- However, lifestyle changes, including weight loss and increased physical activity, can reduce the risk of progression by 40-70%.
- Medications prescribed by healthcare providers can also help prevent or delay the onset of type 2 diabetes.
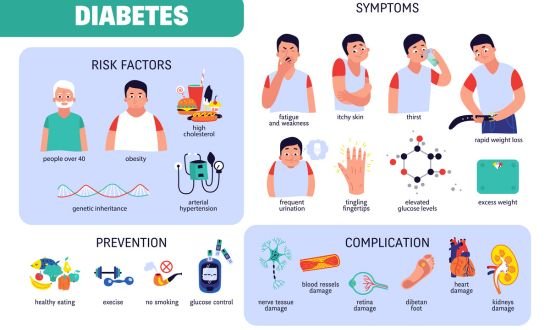
Who’s at Risk?
Prediabetes can affect anyone, but certain factors increase the risk:

- Excess Weight: Being overweight or obese significantly increases the likelihood of prediabetes.
- Sedentary Lifestyle: Lack of physical activity and prolonged periods of sitting are a major risk factor.
- Family History: If you have family history of diabetes you’re more at risk.
- Age Factor: Individuals over 45 are at a higher risk.
- High Blood Pressure: Having hypertension can be a risk factor.
- High Cholesterol: Elevated cholesterol levels may also be a risk factor.
Symptoms of Prediabetes:
In many cases, individuals doesn’t have noticeable symptoms, making it a silent condition.
However, some individuals may experience some signs such as:
- Increased Thirst
- Frequent Urination
- Fatigue
Recommendations for Screening in Adults:
Age for Screening:
In adults, the American Diabetes Association (ADA) recommends screening in individuals of any age who are overweight or obese (a BMI of 25 or higher) and have one or more additional risk factors for diabetes. To check your BMI you can use our BMI calculator.
Risk factors include family history of diabetes, lack of physical activity, high blood pressure, high cholesterol levels, history of gestational diabetes during pregnancy and polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS).
Frequency of Screening:
For adults with no risk factors, screening should begin at age 45. For those with risk factors or if initial tests are normal, screening should be repeated every 3 years. However, if the initial tests indicate pre-diabetes, more frequent monitoring may be necessary.
Recommendations for Screening in Children:
Age for Screening:
Screening in children is not as standardized as in adults. Healthcare providers may consider screening children and adolescents who are overweight or obese, particularly if they have additional risk factors or a family history of diabetes.
Frequency of Screening:
The frequency of screening in children should be determined on a case-by-case basis, taking into account their risk factors, growth and development, and clinical evaluation.
Diagnosis of Prediabetes:
A1C Test:
What It Measures: The A1C test, also known as the hemoglobin A1C test, measures the average blood sugar level over the past two to three months.
Diagnosis Criteria for Adults: An A1C level between 5.7% and 6.4% indicates prediabetes.
Diagnosis Criteria for Children: For children, there isn’t a specific A1C cutoff for prediabetes. It’s typically assessed in conjunction with other tests and clinical evaluation.
Advantages: It doesn’t require fasting, making it more convenient for patients.
Fasting Plasma Glucose (FPG) Test:
What It Measures: This test measures blood sugar levels after an overnight fast (usually 8 hours).
Diagnosis Criteria for Adults: A fasting glucose level between 100-125 mg/dL suggests prediabetes.
Diagnosis Criteria for Children: Similar to adults, a fasting glucose level in this range may indicate pre-diabetes in children.
Advantages: It’s a simple and widely available test.
Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT):
What It Measures: The OGTT involves fasting overnight and then drinking a sugary solution. Blood sugar levels are measured at intervals, typically at 1 and 2 hours after consuming the solution.
Diagnosis Criteria for Adults: A 2-hour glucose level between 140-199 mg/dL indicates pre-diabetes.
Diagnosis Criteria for Children: Similar to adults, a 2-hour glucose level in this range may indicate pre-diabetes in children.
Advantages: It can detect abnormalities in blood sugar regulation more accurately.
Comparison Table of Diagnostic Tests:
| Test | Measures | Diagnosis Criteria | Advantages |
| A1C Test | Average blood sugar | A1C between 5.7% and 6.4% | Convenient (no fasting). |
| Fasting Plasma Glucose | Blood sugar after fasting | Fasting glucose 100-125 mg/dL | Simple and widely available. |
| Oral Glucose Tolerance Test | Blood sugar after glucose | 2-hour glucose 140-199 mg/dL | Detects abnormalities better. |
Complications:
Ignoring prediabetes can have severe consequences. It can lead to several health issues, including:
- Type 2 Diabetes: It can often progresses to type 2 diabetes, requiring lifelong management.
- Cardiovascular Disease: An increased risk of heart disease and stroke.
- Kidney Problems: It can harm your kidneys, leading to kidney disease.
- Neuropathy: Nerve damage can result in numbness, tingling and pain.
- Eye Complications: Retinopathy can cause vision problems and even blindness.
Management of Prediabetes:
Lifestyle Changes:

It can be reversed or managed effectively through lifestyle modifications:
- Healthy Eating: Start eating diets rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Decrease the intake of sugary and processed foods.
- Regular Exercise: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week, such as brisk walking, swimming, or cycling.
- Weight Loss: Even losing a modest amount of weight, like 5-10% of your body weight, can have a significant impact on blood sugar control.
- Smoking Cessation: Quitting smoking can lower your risk of developing diabetes.
Life style changes are the best option in preventing the progression of prediabetes into diabetes. In order to learn more in detail, do follow: https://medicalinquiries.com/diabetes-causes-types-symptoms-and-management/#a-lifestyle-modifications
Medications:
In some cases, lifestyle changes alone may not be sufficient and your healthcare provider may recommend medications to lower your blood sugar levels. These medications can include:
- Metformin: It is a commonly prescribed medication that improves insulin sensitivity and lowers blood sugar.
- GLP-1 Agonists: These drugs help in controlling blood sugar levels by increasing insulin secretion and reducing appetite.
- SGLT-2 Inhibitors: These medications work by increasing glucose excretion through urine.
Prediabetes vs Diabetes:
Understanding the differences between these two conditions is important for managing your health effectively. Following are the differences in tabulated form in order to make it easy for you to understand:
| Aspect | Prediabetes | Diabetes |
| Blood Sugar | Higher than normal, but not high enough for diabetes. | Consistently high |
| Symptoms | Often no symptoms. | Frequent urination, excessive thirst, tired. |
| Management | Lifestyle changes can reverse the condition. | Lifelong management, including medications. |
| Complications | Can lead to type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and more. | Heart disease, kidney disease, blindness, etc. |
Conclusion:
Prediabetes is a warning sign to take care of your health and to prevent yourself from developing diabetes. By making simple lifestyle changes, you can prevent prediabetes from progressing to full-blown diabetes and enjoy a healthier, happier life. Remember, small steps can lead to significant results, so start your journey towards better health today.
Disclaimer
Content on this site is written with thorough research and keeping in mind the latest guidelines. However, no content on this site should substitute professional consultation.
